Comparison for Income Tax Rates in the Philippines – Graduated IT Rates vs 8% IT Rate (With Sample Computations)
Due to the RMC 60-2020 of the Bureau of Internal Revenue, many non-registered sellers and freelancers are called to register and pay taxes. There are Graduated Income Tax Rates, na base lang sa taxable, and 8% Income Tax Rates. This article is for those people or business whose gross sales or receipts (wala pang expenses puro Sales lang) is below PHP 3,000,000 (3M) as its better for that above 3M to have a CPA or accountant. If you were to choose – Graduated IT Rates or 8% IT Rate, read what is better for you!

Taxation became my favorite topic during CPA review classes since my reviewer was so cool. It was way back in 2012; the Train Law was implemented 6 years later. What the Train Law has that was not in our lessons was this 8% option, which you can use instead of the Graduated Rates and Percentage Tax.
I hope you can learn more about it here. P.S. This article is for those NON-VAT and earning less than PHP 3M per year, if you are not one, it’s better to consult your accountant.
- All You Need To Know About the BIR Memo for Online Sellers and Freelancers
- 40+ Websites to Find Digital Nomad Jobs – Work Wherever You Want
- How Filipino Digital Nomads or Online Sellers Can Register to BIR and Pay Taxes
- Valid Philippines ID Guide – How to Apply for a Philippine Postal ID
- Step by Step Guide on How to Pay Your BIR Taxes Online in the Philippines
Table of Contents
Who can Avail the Income Tax Rates?
- Individual Citizens (or Resident Aliens) earning Purely Compensation Income – yung may mga sweldo
- Individuals Engaged in Business – Self-employed, hindi corporation as they usually use 30%, yung online sellers dito
- Practice of Profession – Doctors, Lawyers, Accountants (yung may PRC Card) or athletes, writers, etc. Mga freelancers and yung mostly nag-work from home ay under dito
The default tax rate is the Graduate IT Rates, pwede syang gamitin sa mga lahat sa listahan. However, yung 8% IT rate ay may conditions:
- Purely Self-Employed Individuals and/or Professionals with gross sales/receipts and non-operating income not exceeding PHP 3,000,000
- pure meaning hindi ka mixed earner (example ng mixed-income earner is may sweldo from the company you are working at plus you have sideline na online business)
- you are only taxed 8% in excess of PHP 250,000 – if less than 250K, zero tax mo
- If you are mixed-income earner – for sweldo Graduated Rates are used and for Business Income or Practice of Profession graduated rates or 8% it rates kaso you won’t have 250K deductions, Gross Sales/Receipts multiplied by 8% na yan
Graduated IT Rates Computation
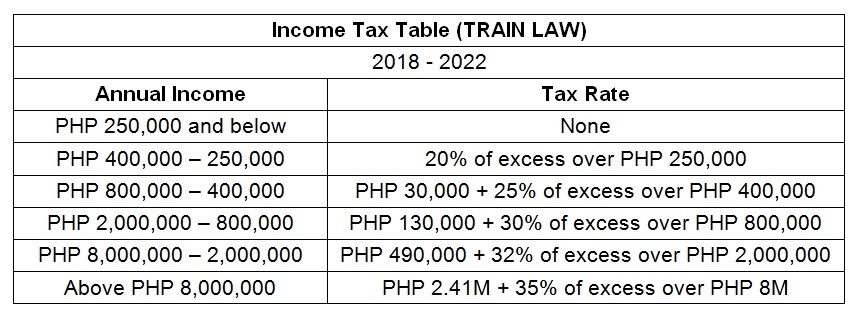
You’ll be using the tax table if you opt for this. If you used this, you could choose between Itemized Deductions and Optional Standard Deduction. You will also be asked to file 3% Percentage tax.
The formula is usually:
Gross Sales / Receipts – Cost of Sales/Services = Gross Income – Deductions = Net Income
With Itemized Deductions
Itemized Deductions are the expenses that are allowed to be deducted to your gross income. The usual are:
- Depreciation – if you have buildings or equipment)
- Contributions – SSS, Philhealth, HDMF
- Taxes and Licenses – yung binayad mo sa BIR at sa pagkuha ng Mayor’s Permit, etc.
- Transportation and Travel
Please note that not all can be used under Itemized deductions, like professional fees na walang withholding tax or personal items na hindi para sa negosyo.
Gross Sales/Receipts – Yung sales nyo for the whole quarter or year, wala pang deductions or total fee from your client
Less Cost of Sales or Services – For sellers, it’s usually Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory, for services, you can use your direct cost and expenses.
It will equal to Gross Income.
You can also additionally deduct that in itemized deductions to have your Net Income. Net Income will be used as the basis for your Income Tax.
Example 1:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 400,000
Less COS: – 150,000
Gross Income = PHP 250,000
Itemized Deductions – 50,000
Net Income PHP 200,000
Tax Due PHP 0
Why is tax due zero? Because hindi sya naka abot sa 250,000 as per the tax table.
Example 2 :
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 500,000
Less COS: – 150,000
Gross Income = PHP 350,000
Itemized Deductions – 50,000
Net Income PHP 300,000
Tax Due PHP 10,000
Why is it 10k? Net Income is PHP 300K; when you see the tax table, it says 20% in excess of 250K. So 300K – 250K = 50K x 20% = 10K.
This is a bit tedious, and you need to be careful with the deductions and computation of COS. When you get audited, especially if your income is high but you have zero tax due, and the BIR officers saw that you erroneously considered a few expenses as Itemized, but it’s really not, then you get to pay the penalty and the correct tax. It’s better to consult with a bookkeeper or accountant if you opt for this.
Please also note that with Itemized deductions, you will need to pass an income statement and financial statement during your Annual Income Tax Return.
With Optional Standard Deduction
OSD is quite simple. You will have a 40% deduction of your gross sales or receipts; the rest is net income—no more computation of Cost of Sales or Services or Itemized deductions. Also, you won’t submit a Financial Statement or Income Statement to the BIR, unlike the Itemized deduction.
Example 1:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 400,000
OSD – 160,000
Net Income PHP 240,000
Tax Due PHP 0
Why is tax due zero? Because hindi sya naka abot sa 250,000 as per the tax table.
Example 2:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 500,000
OSD – 200,000
Net Income PHP 300,000
Tax Due PHP 10,000
Computation is per tax table.
Percentage Tax Computation
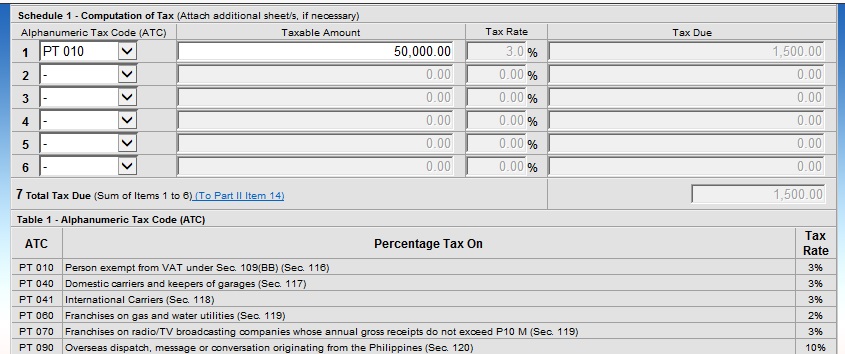
Please note you will also be paying percentage tax, which is the 2551Q every quarter and year. It will be 3% of your gross sales or receipts.
Example:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 50,000 x 3% = 1,500
8% IT Rates Computation
For the 8%, IT rate it’s pretty easy. It’s 8% Income Tax on Gross Sales/Receipts instead of Graduated IT Rates and Percentage Tax. Meaning wala ng percentage tax (2551), yung income tax nalang (1701).
However, wala na tong deductions like Itemized or OSD. You can have PHP 250,000 deduction if you are a purely self-employed and/or professional with gross below PHP 3M. If you are mixed, may sweldo at may sideline na online business, you won’t have PHP 250,000 deduction.
Example 1 for pure income earners:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 300,000
Deduction – 250,000
Taxable Income PHP 50,000
Tax Due PHP 4,000
It’s Taxable Income multiplied by 8%—no need to refer to the tax table.
Example 2 for mixed-income earners:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 300,000
Deduction – 0
Taxable Income PHP 300,000
Tax Due PHP 24,000
For the business income lang yan, hindi pa kasama yung tax sa sweldo.
Example 3 for pure income earners:
Gross Sales or Receipts: PHP 400,000
Deduction – 250,000
Taxable Income PHP 150,000
Tax Due PHP 12,000
Comparison of Payments
You should note that Graduated IT Rates – you will pay income tax and percentage tax, but you can claim deductions.
For 8% – no need to pay 3% percentage tax and you can only claim PHP 250,000 allowable reduction if you are a pure income earner.
Comparison 1:
For Graduated
Percentage Tax = 250,000 * .03 = 7,500
Income Tax = 250,000 – 100,000 (OSD) = 150,000 = Zero
For 8%
Percentage Tax = None
Income Tax = 250,000 – 250,000 = 0 = Zero
Comparison 2:
For Graduated
Percentage Tax = 300,000 * .03 = 9,000
Income Tax = 300,000 – 120,000 (OSD) = 180,000 = Zero
For 8%
Percentage Tax = None
Income Tax = 300,000 – 250,000 = 50,000 * .08 = 4,000
Comparison 3:
For Graduated
Percentage Tax = 400,000 * .03 = 12,000
Income Tax = 400,000 – 160,000 (OSD) = 240,000 = Zero
For 8%
Percentage Tax = None
Income Tax = 400,000 – 250,000 = 150,000 * .08 = 12,000
Comparison 4:
For Graduated
Percentage Tax = 500,000 * .03 = 15,000
Income Tax = 500,000 – 200,000 (OSD) = 300,000 = 10,000
For 8%
Percentage Tax = None
Income Tax = 500,000 – 250,000 = 250,000 * .08 = 20,000
Example 5:
For Graduated
Percentage Tax = 500,000 * .03 = 15,000
Income Tax = 500,000 – 250,000 (COS and Itemized Deductions) = 250,000 = Zero
For 8%
Percentage Tax = None
Income Tax = 500,000 – 250,000 = 250,000 * .08 = 20,000
Example 6:
For Graduated
Percentage Tax = 1,000,000 * .03 = 30,000
Income Tax = 1,000,000 – 600,000 (COS and Itemized) = 400,000 = 30,000
For 8%
Percentage Tax = None
Income Tax = 1,000,000 – 250,000 = 750,000 * .08 = 60,000

What is better depends on your business – the flow of your income and expenses. As you can see for those who earn about 400,000 per year, you can choose either of the two and end up paying the same (especially if you have OSD or your taxable income does not exceed 250K). However, if it’s lower, an 8% advantage, but if higher, it will depend on your net income too.
Please note that you can only choose one as you start the year. You can’t transfer from Graduated to 8% or vice versa. I hope you are enlightened in which is better; Graduated IT Rates or 8% IT Rate. You can also read how to pay online and how to file your taxes.

Are you on Pinterest? Pin these!

About the Writer

Hey, I’m Lyza! I once was a person who just imagined going to places “one day” but decided to pursue my dreams. My first travel abroad was in Japan, solo, last 2018, and fell in love with the journey since. I’m aiming to visit 10 countries before turning 30 and 2 new places in the Philippines every year. Besides traveling, I love organizing trips, photography, reading, and making new friends. Follow my adventures through my Instagram.



Hi po,
yung busines po namin is mid-class barbershop. yung gross po namin is around 40-45k lang po.. pipiliin ko po ba yung 8% ? if yes, what if yung na file ko before sa 2551q is graduated sales and mag file po ako ulit ng form 1701q tapos yung pipiliin ko na is yung 8% since di naman kami nag eexceed ng 3M/year.. okay lang po ba yun?
Good day po. Required po mag file quarterly kung Graduated ang pinili ko?
Hi po, Do i need to file receipt and register un mga journals and ledgers if i opted for the 8% income tax rate. salamat
Thank you Ma’am Lyza for the info!
Ask ko lng po Ma’am, if you choose to avail the 8% Income Tax Rate, is it still required to submit FS during annual?
Hi Ms. Lyza..
thank you for sharing your thoughts..sobrang helpful kc if you’re going to ask bir people…tipid” sumagot…easy to say “get a bookkeeper”…nagtititpid ka nga eh…sa gaya ko a newbie….and earning less … of course aralin mo na lang…and I can!!! with the help of good people like you na, hindi madamot mag-share ng thoughts in a “VERY SIMPLE” way to understand…
More power!
Thank you for this! Mas madali na sya intindihin. Huhu. Question ko lang po, bakit po 8% yung napili nila at hindi other value, eg 5%, 6%, 7%, etc.
baka study po yan ng BIR po …
Hi i would like to ask what method should i use in filing my bir. Is it the graduated or 8%. I have approx 70k gross monthly income for trucking. Pls guide me in this. Thanks
It depends on you po or you can check your COR. Basta, 1 type lang in a year – di pwede pa iba-iba.
Hello. I’d like to ask paano po kapag lower than 250k yung naging gross receipts? Since part time lang sya, hindi aabot. Does that mean that it will follow comparison #1? Thank you.
Parang ganun po 🙂
Just want to ask, pano if ung TIN mo is for individuals earning purely compensation income (BIR form 1902) then this year consultant ka nlng (self-employed).. Pwd kayang i-avail ang 8% income tax rate? If yes, do I need to amend my TIN or need to get a new TIN? Hope you can answer this. Thanks ?
mag.register sa BIR as self-employed pa using 1901 pero pero your old TIN will be used, don’t forget na i check mo yun 8% po.
Hi, just want to ask if the monthly amortization of mortgaged rental property can be deducted from the taxable rental net income?
If the expense is related to your business, I think you can. However, you can ask your bookkeeper about it